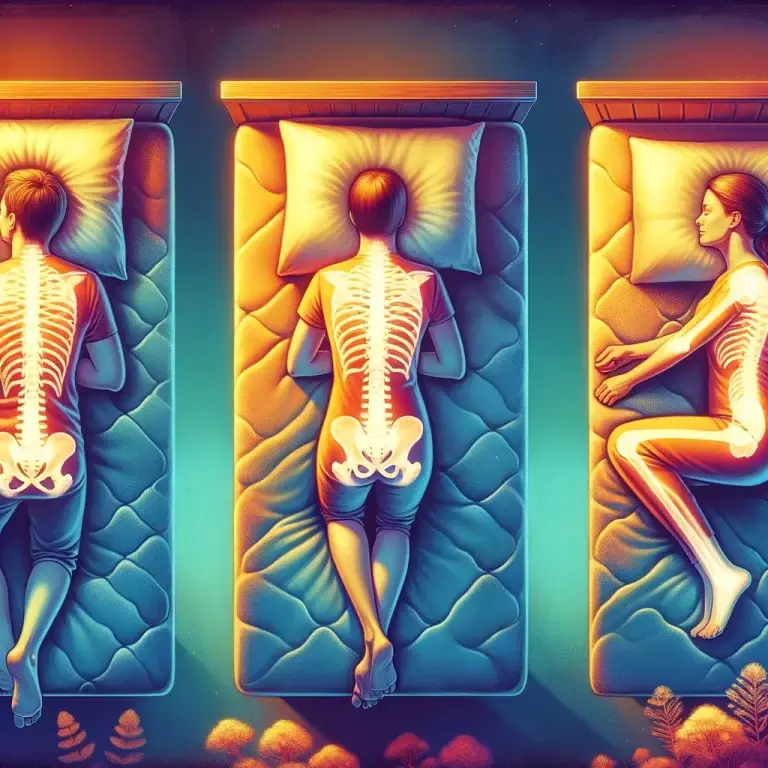
Which Sleeping Position Is Best for You?
Ever wondered which sleeping position is best for a good night’s rest? The way you position yourself during sleep can significantly impact your overall health, from spinal alignment to digestion and even snoring. Let’s explore the pros and cons of the most common sleeping positions to help you find the best fit for your body and lifestyle.
Sleeping on Your Front
Sleeping on your front, also known as the prone position, can feel cozy for some, but it isn’t the most health-friendly choice. Here's why:
The Drawbacks
- Spine and Neck Health: Lying face down forces your neck to twist to one side, which can lead to discomfort or stiffness over time. Additionally, the lower back may experience strain due to the unnatural curve of the spine.
- Airflow Restriction: This position may restrict airflow, making it a less favorable choice for individuals prone to snoring or sleep apnea. Restricted breathing can decrease sleep quality and leave you feeling less rested.
- Facial Pressure: Pressing your face into a pillow can cause skin irritation or even contribute to wrinkles in the long run.
Why People Choose It: Despite its drawbacks, some individuals gravitate toward this position for its comfort or out of habit. For stomach sleepers, small adjustments like using a thin pillow under the hips can help alleviate pressure on the spine and improve alignment.
Learn more about why stomach sleeping isn't ideal for spinal health from the Sleep Foundation [4].
Sleeping on Your Side
Side sleeping is one of the most popular positions worldwide. It offers numerous health benefits and is often recommended for individuals dealing with specific health issues.
Benefits of Side Sleeping
- Improved Digestion: Research suggests that sleeping on the left side can reduce acid reflux and aid digestion. This is because it prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus, a phenomenon known as gastroesophageal reflux. [2]
- Reduced Snoring and Sleep Apnea: Side sleeping helps keep the airways open, reducing the likelihood of snoring or obstructive sleep apnea episodes. [4]
- Heart Health: This position, especially on the left side, enhances blood circulation and is often advised for pregnant women to improve fetal health. It also reduces pressure on the vena cava, a major vein responsible for returning blood to the heart. [3]
- Spinal Support: When combined with a supportive pillow and proper positioning, side sleeping promotes spinal alignment and prevents discomfort.
Tips for Optimal Side Sleeping
- Use a pillow that fills the gap between your shoulder and neck to keep your spine neutral.
- Placing a pillow between your knees can further enhance alignment and reduce stress on the hips and lower back.
- Alternate between sides to avoid muscle imbalances or pressure points.
Check out more tips for side sleepers from Healthline [8].
Sleeping on Your Back
Sleeping on your back is widely considered the healthiest sleeping position by experts. Here’s why it’s often the top recommendation:
Advantages
- Neutral Spine Alignment: This position naturally supports the spine, distributing weight evenly and reducing pressure points.
- Minimized Wrinkles: Unlike stomach or side sleeping, back sleeping minimizes direct pressure on the face, reducing the risk of sleep-related wrinkles.
- Relaxed Muscles: Lying on your back allows muscles and joints to rest in their natural alignment, which can ease tension and promote recovery.
Challenges
- Snoring and Sleep Apnea: Sleeping on your back can exacerbate these conditions as gravity may cause the tongue and soft tissues to block the airway.
- Lower Back Pain: Without proper support, some individuals may experience discomfort in the lumbar region.
Tips for Back Sleepers
- Use a pillow that supports the natural curve of your neck and keeps your head aligned with your spine.
- Place a small pillow or rolled towel under your knees to maintain the natural curve of your lower back.
Discover why back sleeping is so beneficial for spinal health at Houston Methodist [7].
The Science Behind Sleeping Positions
Your preferred sleeping position is often influenced by factors like age, body type, and health conditions. Here’s how each factor plays a role:
Age
As we age, sleep preferences can change. For example, infants naturally sleep on their backs for safety reasons, while older adults may favor side sleeping to alleviate joint pain.
Health Conditions
- Pregnancy: Side sleeping, particularly on the left, is recommended to optimize blood flow and reduce pressure on internal organs. [3]
- Digestive Issues: Left-side sleeping is preferred for those with acid reflux or heartburn. [2]
- Chronic Pain: Individuals with back pain often benefit from back or side sleeping, provided they use supportive bedding.
Conclusion
Your sleeping position plays a pivotal role in your overall health and well-being. While each position has its pros and cons, understanding their impact can help you make informed choices. Whether you’re a side sleeper seeking better spinal support, a back sleeper enjoying a neutral spine, or a stomach sleeper looking to transition, there are ways to optimize your sleep quality.
For more insights into posture and sleep, explore our free tools and guides designed to help you rest better and wake up refreshed.
